《Units ICT Short Course》
This module introduces students to the basic components of computer systems—hardware and software. At Rockview University, we focus on helping students understand how computers work and how we interact with them. The course is divided into clear, easy-to-follow units that build a strong foundation in ICT.
UNIT 1. Introduction to Computers
1. What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic machine that helps us do tasks like typing, calculating, watching videos, and browsing the internet. It works by receiving data, storing it, processing it, and showing the results.
- Used for: Learning, working, playing games, communication
- Main parts: Input, storage, processor, output

2. How a Computer Works
Step 1: Input Data
Input means giving information to the computer. You do this using input devices.
- Devices: Keyboard, mouse, scanner, microphone
- What happens: The device sends signals to the computer to tell it what to do

Step 2: Store Data
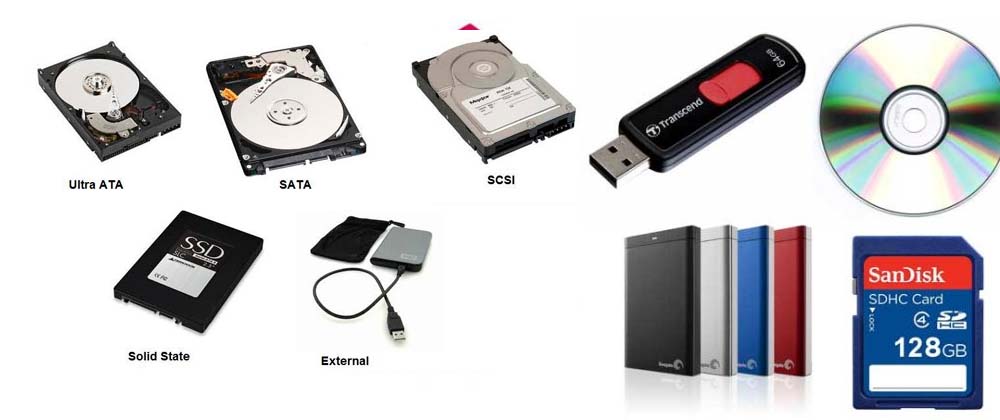
Storage means saving information so you can use it later. Computers store data using special devices.
- Devices: Hard Disk Drive (HDD), Solid-State Drive (SSD), Flash Drive (USB)
- What happens: Data is saved as 0s and 1s (binary code)

Step 3: Process Data
Processing means working with the data to get results. The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of the computer.
- Parts of CPU:
- ALU – does math and logic
- Control Unit – manages how data moves
- What happens: The CPU follows instructions to calculate, compare, and change data
Step 4: Output Data
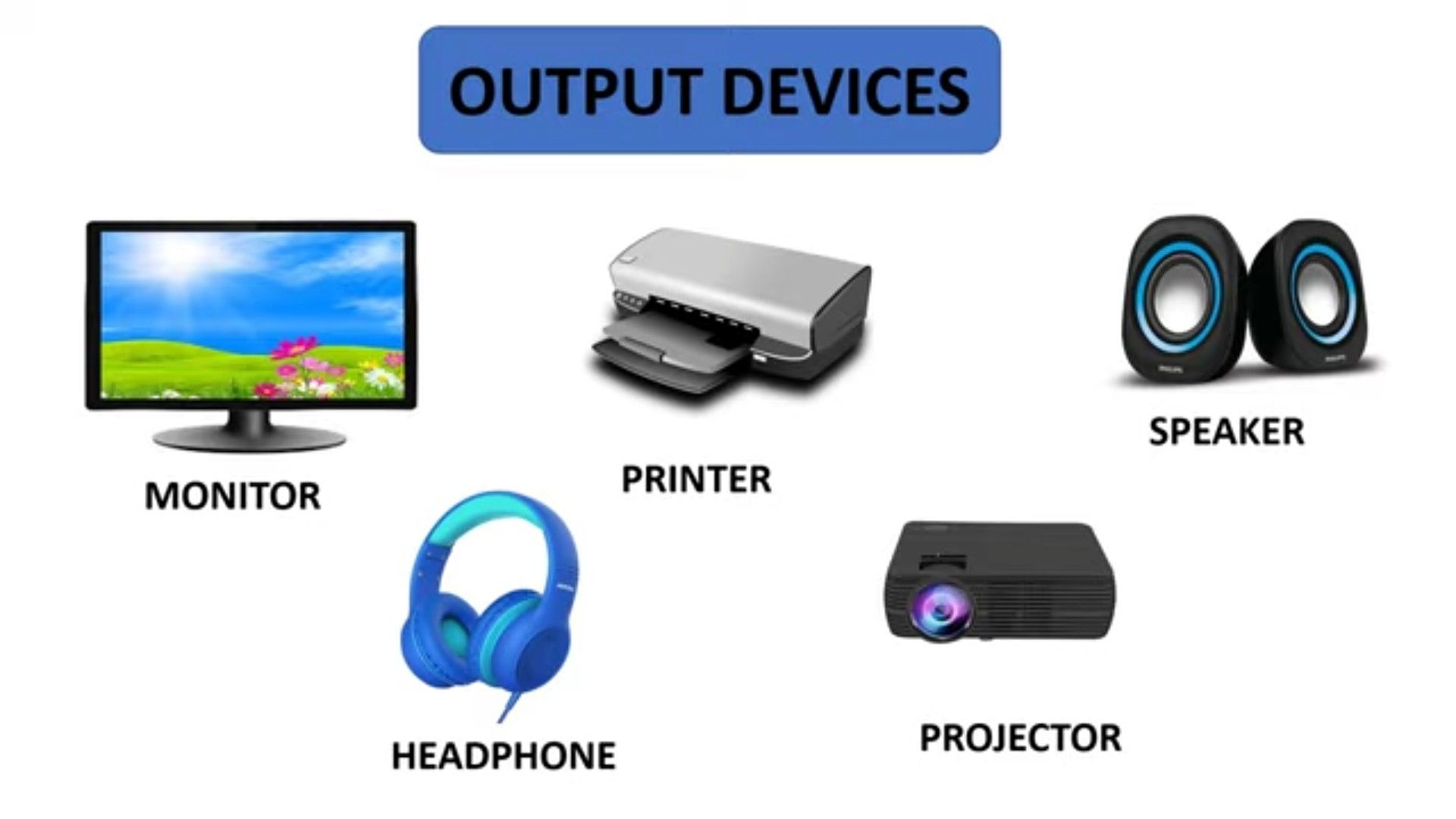
Output means showing the results of the processed data. Output devices help you see or hear the results.
- Devices: Monitor, printer, speakers
- What happens: The computer sends results to the output device in a way you can understand
3. Summary
A computer works in four main steps: it takes input from devices, stores the data, processes it using the CPU, and gives output through devices like a monitor or printer. These steps help us use computers for learning, working, and having fun.
Unit 2: Computer Hardware and software
1. Computer Hardware
Hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer that you can touch and see. These include input devices (like keyboards and mice), output devices (like monitors and printers), and internal components (like the CPU and system unit).
2. Common Hardware Devices
Keyboard
A keyboard is used to type text and give commands to the computer.
- Functions: Typing, navigation, and control using special keys (e.g., Ctrl, Alt).
- Types: Wired Keyboard, Wireless Keyboard
- Characteristics:
- Wired: Reliable connection, no battery needed
- Wireless: Portable, less cable clutter, needs batteries or charging

Wireless Mouse

Wired Mouse
Mouse
A mouse is a pointing device used to move the cursor and interact with items on the screen.
- Functions: Cursor control, selection, and navigation.
- Types: Wired Mouse, Wireless Mouse
- Characteristics:
- Wired: Stable connection, no charging required
- Wireless: More flexible movement, requires batteries or charging

Wireless Keyboard

Wired Keyboard
Monitor
A monitor displays the visual output from the computer, such as text, images, and videos.
- Functions: Viewing content, adjusting resolution, displaying user interface.
- Characteristics: Varies in size, resolution (HD, Full HD, 4K), and display type (LCD, LED).

Printer
A printer produces physical (hard copy) documents and images from your computer.
- Functions: Printing documents, photos, and graphics.
- Types: Inkjet Printer, Laser Printer
- Characteristics:
- Inkjet: Good for color images, lower cost, slower
- Laser: Fast printing, better for text, higher upfront cost

Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is the brain of the computer. It processes instructions and manages tasks.
- Functions: Executes instructions, performs calculations, controls system operations.
- Characteristics: Measured in GHz (speed), has multiple cores for multitasking.

System Unit
The system unit is the main body of a desktop computer. It contains the CPU, memory, and other internal components.
- Functions: Houses and protects internal hardware, supports upgrades.
- Characteristics: Includes motherboard, power supply, storage drives, and expansion slots.

Computer Software
1. What is Software?
Software is a set of instructions or programs that tell a computer what to do. Unlike hardware, software is not physical—you can't touch it. It controls how the computer works and helps users perform tasks.
2. Main Categories of Software
System Software
System software manages the computer's hardware and provides a platform for other software to run. It includes operating systems like Windows and MacOS.
- Functions: Controls hardware, manages memory and files, ensures system security.
- Examples: Windows 11, MacOS
- Characteristics:
- Essential for running the computer
- Works in the background
- Starts automatically when the computer is turned on

Computer Software
Application Software
Application software helps users perform specific tasks like writing documents, browsing the internet, or editing images.
- Functions: Increases productivity, provides entertainment, supports communication.
- Examples: Microsoft Word, Google Chrome, Adobe Photoshop
- Characteristics:
- User-friendly interfaces
- Designed for specific tasks
- Can be installed or accessed online

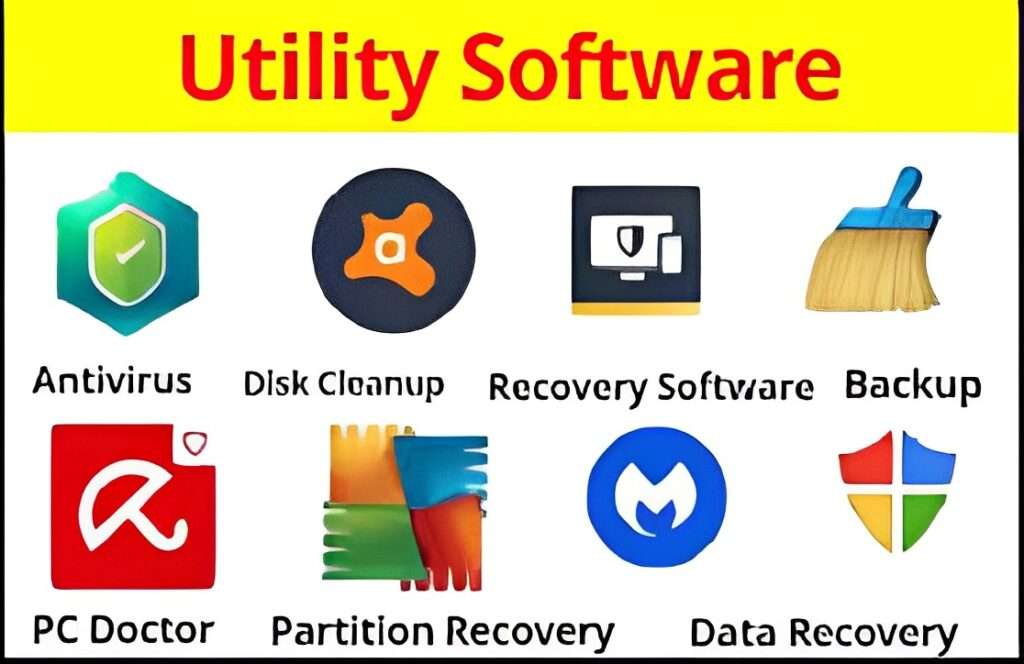
Utility Software
Utility software helps maintain and improve the performance of your computer. It includes tools for cleaning, protecting, and backing up your system.
- Functions: Disk cleanup, virus protection, system optimization, backup and recovery.
- Examples: Avast Antivirus, 360 Total Security
- Characteristics:
- Often runs in the background
- Improves speed and safety
- Can be scheduled to run automatically
Programming Software
Programming software is used by developers to create, test, and debug other software. It includes code editors, compilers, and development environments.
- Functions: Code editing, compiling, debugging, project management, testing.
- Examples: Visual Studio Code, C++ Compiler
- Characteristics:
- Supports multiple programming languages
- Provides tools for writing and testing code
- Used mainly by software developers

3. Summary
Software is essential for making computers useful. System software runs the computer, application software helps users complete tasks, utility software keeps the system healthy, and programming software builds new tools. Together, these software types allow us to work, learn, communicate, and create.
UNIT 3. Understanding Operating Systems
1. What is an Operating System (OS)?
An operating system is the main software that helps a computer or device work. It controls how the system starts, runs apps, saves files, and connects to other devices. Without an OS, the computer or phone cannot function.
2. Functions of an Operating System
- Starts the device: Loads when you turn it on.
- Runs applications: Opens and manages programs like Word or Chrome.
- Manages files: Helps you save, open, and organize documents.
- Controls hardware: Connects to printers, keyboards, screens, etc.
- Provides security: Protects your system from viruses and errors.
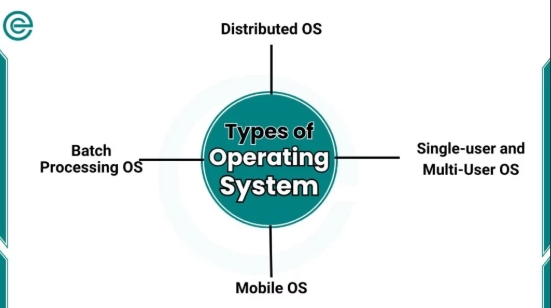
3. Types of Operating Systems
Single-User Operating System
Allows one person to use the computer at a time. Most personal computers use this type.
- Examples: Windows 10, macOS Ventura
- Used in: Homes, schools, offices
Multi-User Operating System
Allows many users to access the same system at once. Common in servers and large organizations.
- Examples: Linux (Ubuntu Server), UNIX
- Used in: Companies, universities, data centers
Mobile Operating System
Designed for smartphones and tablets. It helps run apps, manage touchscreens, and connect to mobile networks.
- Examples: Android, iOS
- Used in: Phones, tablets
Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
Used in machines that need fast and accurate responses, like robots or medical devices.
- Examples: FreeRTOS, VxWorks
- Used in: Robots, airplanes, medical tools
4. Examples of Operating Systems
Windows
A popular OS used in schools, offices, and homes. It is easy to use and supports many programs.
- Examples: Windows 10, Windows 11
- Used in: Laptops, desktops

macOS
Made by Apple for Mac computers. Known for its clean design and strong security.
- Examples: macOS Monterey, macOS Ventura
- Used in: Apple laptops and desktops

Linux
A free and open-source OS used by programmers and companies. It is flexible and secure.
- Examples: Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian
- Used in: Servers, schools, tech companies

Android
A mobile OS used in smartphones and tablets. It supports many apps and is easy to customize.
- Android Examples: Android 12, Android 13 etc.
- Iphone Examples: Iphone 12, iphone 15 etc.
- Used in: Samsung, Tecno, Huawei, iphones and other mobile phones

5. Summary
Operating systems help computers and devices work properly. They manage apps, files, and hardware. Types include single-user, multi-user, mobile, and real-time OS. Examples include Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Each OS is designed for different devices and user needs.
UNIT 4. Working with Files and Folders
1. What Are Files and Folders?
A file is something you create or use on a computer. It can be a document, picture, video, song, or any saved work. A folder is like a digital container that holds files. It helps you keep your work neat and organized.
- Files: Homework, photos, music, videos, notes
- Folders: Used to group related files together (e.g., "School Work", "Family Photos")

2. Types of Files
- Text files: .docx, .txt, .pdf
- Image files: .jpg, .png
- Video files: .mp4, .avi
- Audio files: .mp3, .wav
3. Basic Actions You Can Do
Create a New File or Folder
You can make a new file using programs like Microsoft Word or Paint. To create a folder, right-click on the desktop or inside a folder and choose “New Folder.”
- Why: To start new work or organize your files
- Tip: Give your folder a name that tells what’s inside
Save Your Work
Saving keeps your work safe. If you don’t save, you might lose everything. Use “Save” to update your file or “Save As” to make a copy with a new name.
- Shortcut: Press
Ctrl + Sto save quickly - Tip: Save often while working
Rename a File or Folder
Renaming helps you know what a file or folder is about. Right-click the item, choose “Rename,” and type a new name.
- Why: To make names clear and easy to find
- Tip: Don’t use symbols like / \ * ? in names
Delete a File or Folder
Deleting removes things you no longer need. They go to the Recycle Bin first, so you can get them back if needed.
- How: Right-click > Delete or press the
Deletekey - Tip: Empty the Recycle Bin to free up space
Move Files into Folders
Moving helps you organize your work. You can drag a file into a folder or use copy and paste.
- Why: To keep your computer neat and tidy
- Tip: Group similar files together (e.g., all schoolwork in one folder)

4. Summary
Files are where your work is saved—like documents, pictures, and videos. Folders help you keep those files organized. Learning how to create, save, rename, delete, and move files makes using a computer easier and more fun.
UNIT 5. Introduction to Microsoft Word
1. What is Microsoft Word?
Microsoft Word is a computer program used to write and edit documents. You can use it to type letters, school work, notes, and more. It helps you make your writing look neat and professional.
- Used for: Writing, editing, formatting, printing documents
- Common file type: .docx

2. Key Features of Microsoft Word
Typing and Formatting Text
You can type words and change how they look. Formatting means making text bold, italic, or underlined.
- Bold: Makes text darker and stronger
- Italic: Slants the text
- Underline: Adds a line under the text
- Font: Change the style and size of letters
Adding Pictures and Tables
You can insert pictures to make your document more interesting. Tables help you organize information in rows and columns.
- Insert Picture: Add images from your computer
- Insert Table: Create a grid to show data clearly
Saving and Printing
Saving keeps your work safe. Printing lets you get a paper copy of your document.
- Save: Use
Ctrl + Sor click the Save icon - Print: Go to File > Print to choose printer and settings

3. Summary
Microsoft Word is a powerful tool for writing and editing documents. You can type, format text, add pictures and tables, save your work, and print it. These features help you create neat and professional-looking documents for school, work, or personal use.
UNIT 6. Microsoft Excel Basics
1. What is Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a computer program used to work with numbers and information. It helps you organize data, do calculations, and create charts. Excel is useful for school, business, and everyday tasks like budgeting.
- Used for: Math, data entry, record keeping, analysis
- Common file type: .xlsx
2. Main Features of Excel
Rows and Columns
Excel uses a grid made of rows (side to side) and columns (up and down). Each box in the grid is called a cell, and you can type numbers or words into it.
- Rows: Labeled with numbers (1, 2, 3…)
- Columns: Labeled with letters (A, B, C…)
- Cells: Where data is entered (e.g., A1, B2)
Basic Calculations
Excel can do simple math like adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing. You can use formulas to do the work for you.
- Addition:
=A1 + B1 - Subtraction:
=A1 - B1 - Multiplication:
=A1 * B1 - Division:
=A1 / B1
Creating Charts
Charts help you see your data in a visual way. Excel can turn numbers into bar charts, pie charts, and line graphs.
- Bar Chart: Shows data with bars
- Pie Chart: Shows parts of a whole
- Line Chart: Shows changes over time
3. Summary
Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool for working with numbers and data. You can organize information using rows and columns, do calculations with formulas, and create charts to understand your data better. Excel makes math and data easy to manage and fun to explore.
UNIT 7. Internet and Browsing
1. What is the Internet?
The internet is a global network that connects millions of computers and devices. It lets people share information, send messages, watch videos, play games, and learn new things. You can use the internet at home, school, or on your phone.
- Used for: Research, communication, entertainment, shopping, learning
- Examples: Google, YouTube, Wikipedia, Facebook

2. What is a Web Browser?
A web browser is a program that helps you visit websites on the internet. It shows you pages, pictures, videos, and links.
- Popular browsers: Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Safari
- Browser icon: Click the browser icon to open it

3. How to Browse the Internet
Step 1: Open a Browser
Click on a browser like Chrome or Edge to start browsing.
Step 2: Type a Website Address or Search
You can type a website address (like www.google.com) or search for something using keywords
(like “how to draw”).
Step 3: Click Links to Explore
Websites have links you can click to go to other pages, watch videos, or read more. Just click and explore!
- Tip: Use the back button to return to the previous page
- Tip: Use bookmarks to save favorite websites

4. Summary
The internet connects computers around the world and helps you find information, learn, and have fun. You use a browser like Chrome or Edge to visit websites. Just type what you want to see, click on links, and explore the web safely and smartly.
UNIT 8.Email Essentials
1. What is Email?
Email (short for electronic mail) is a way to send and receive messages using the internet. You can use email to talk to friends, teachers, or workmates—anywhere in the world. It’s fast, free, and easy to use.
- Used for: Sending messages, documents, pictures, and links
- Examples of email services: Gmail, Yahoo Mail, Outlook

2. Steps to Send an Email
Step 1: Create an Email Account
To use email, you need an account. You can sign up for free on websites like Gmail.com or Outlook.com. You’ll choose a username and password to log in.
- Example: yourname@gmail.com
- Tip: Use a password that is easy to remember but hard for others to guess
Step 2: Write a Message
Click “Compose” or “New Message” to start writing. Type the email address of the person you want to send it to, add a subject (title), and write your message.
- To: The person’s email address (e.g., teacher@example.com)
- Subject: A short title for your message (e.g., Homework Submission)
- Message: The main text you want to send
Step 3: Click “Send”
After writing your message, click the Send button. Your email will be delivered in seconds.
- Tip: Double-check the email address before sending
Step 4: Check Your Inbox
The inbox is where you receive emails. Open it to read replies or new messages. You can also reply, delete, or move messages to folders.
- Inbox: Where new messages arrive
- Sent: Shows emails you’ve sent
- Drafts: Unfinished messages saved for later
3. Summary
Email is a simple and fast way to send messages online. First, create an account. Then write your message, add a subject, and click “Send.” Always check your inbox for replies. Email helps you stay connected with others anytime, anywhere.
UNIT 9.Basic Computer Security
1. What is Computer Security?
Computer security means protecting your computer and personal information from harm. It helps keep your files safe, your passwords private, and your device free from viruses. Good security habits help you stay safe while using the internet.
- Used for: Protecting data, avoiding scams, keeping devices healthy
- Important for: Students, families, businesses, everyone online

2. How to Stay Safe Online
Use Strong Passwords
A strong password is hard to guess. It should have letters, numbers, and symbols. Never share your password with others.
- Example:
Rockview@2025! - Tip: Don’t use your name or birthday as a password
Avoid Unknown Links and Downloads
Don’t click on links or download files from strangers or suspicious websites. They might contain harmful software or tricks to steal your information.
- Tip: Only download from trusted websites
- Tip: Ask an adult or teacher if unsure
Install Antivirus Software
Antivirus software protects your computer from harmful programs. It scans your system and removes threats before they cause damage.
- Examples: Avast, 360 Total Security, Windows Defender
- Tip: Keep your antivirus updated regularly

3. Common Security Threats
Viruses
Viruses are harmful programs that can damage your computer or steal your data. They often come from unsafe downloads or infected USB drives.
- Effect: Slow computer, lost files, strange behavior
- Protection: Use antivirus and avoid unknown files
Phishing
Phishing is when someone sends fake emails or messages to trick you. They may ask for your password or personal details.
- Example: “Click here to win a prize!”
- Tip: Never give your password or click suspicious links

4. Summary
Computer security helps protect your device and personal information. Use strong passwords, avoid unknown links, and install antivirus software. Watch out for viruses and phishing scams, and always think before you click. Staying safe online is important for everyone.
UNIT 10. Basic Troubleshooting
1. What is Troubleshooting?
Troubleshooting means finding and fixing problems with your computer. If something isn’t working right—like a slow system or a blank screen—you can try simple steps to solve it. These steps help your computer run better and save you time.
- Used for: Solving computer issues, improving performance
- Important for: Students, teachers, office workers, everyone who uses a computer

2. Common Problems and Simple Fixes
Computer is Slow
If your computer is running slowly, try restarting it. This clears temporary files and refreshes the system.
- Fix: Click Start > Power > Restart
- Tip: Close unused programs before restarting
Device Not Working
If your mouse, keyboard, or printer isn’t working, check the cables. Make sure everything is plugged in properly.
- Fix: Unplug and plug back in
- Tip: Try a different USB port
Software Has Errors
If a program keeps crashing or showing errors, it might need an update. Updates fix bugs and improve performance.
- Fix: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Check for updates
- Tip: Keep your system and apps updated regularly
3. Helpful Tips
If you’re not sure what to do, ask a teacher, parent, or tech expert for help. You can also search online for solutions using trusted websites or video tutorials.
- Tip: Use Google or YouTube to find step-by-step guides
- Tip: Write down the error message to help find answers
4. Summary
Troubleshooting helps you fix common computer problems like slow speed, device errors, and software bugs. Restarting, checking cables, and updating software are easy steps anyone can try. If you’re unsure, ask for help or search online. Learning to troubleshoot makes you a smarter computer user.